Advantages Of Flexible Exchange Rate
Floating Exchange Rate
An exchange rate organisation where a country's currency price is determined past the relative supply and demand of other currencies
What is a Floating Exchange Charge per unit?
A floating substitution rate is an exchange charge per unit organisation where a land's currency price is determined by the foreign exchange market, depending on the relative supply and demand of other currencies. A floating exchange rate is not restrained past trade limits or government controls, different a fixed exchange rate.

Summary
- A floating commutation charge per unit refers to an exchange rate system where a land's currency price is adamant past the relative supply and demand of other currencies.
- Currencies with floating commutation rates tin exist traded without any restrictions, dissimilar currencies with fixed commutation rates.
- Although the floating exchange rate is non entirely determined by the government and fundamental banks, they tin intervene to proceed the currency at a favorable toll for global merchandise.
Functions of a Floating Exchange Rate
A floating exchange charge per unit functions in an open up market where speculations, along with demand and supply forces, drive the price. Floating exchange charge per unit structures mean that changes in long-term currency prices represent comparative economic strength and differences in interest rates across countries. Changes in the short-term floating commutation rate correspond disasters, speculations, and the daily supply and need of the currency.
In the graph below, an increased currency supply from S1 to S2 at the same need D1 implies that the currency-pair price will depreciate. In contrast, increased demand from D1 to D2 at the same supply S1 volition lead to currency appreciation.
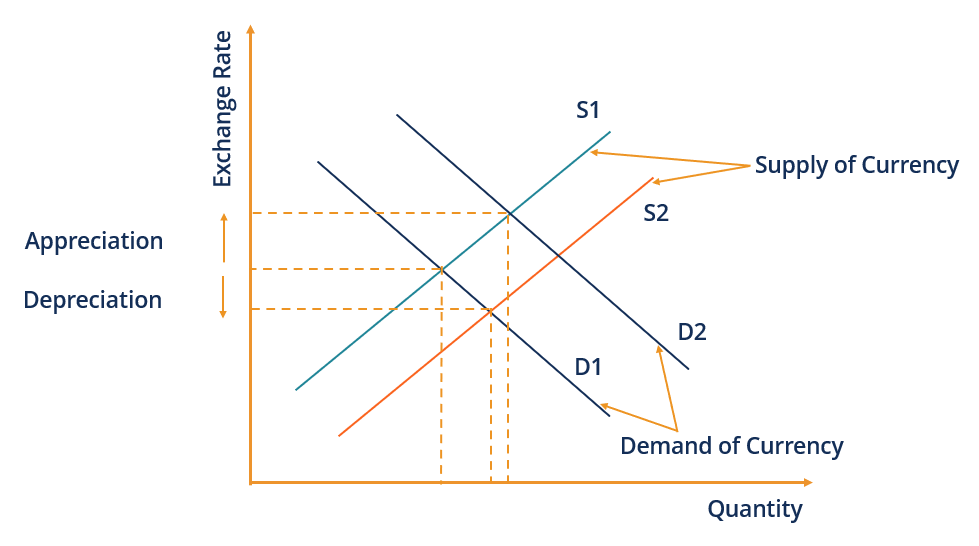
Market sentiment towards the economic system of a country affects how potent or weak the floating currency is perceived. For example, a country's currency is expected to depreciate if the market views the government equally unstable. Although the floating exchange rate is not entirely determined past the government, they tin can arbitrate when the currency is too depression or too high to keep the currency at a favorable toll.
Benefits of a Floating Exchange Charge per unit
1. Stability in the balance of payments (BOP)
A remainder of payments is in the statement of transactions between entities of a state and the entities of the rest of the world over a time flow. In theory, whatever imbalance in that statement automatically changes the commutation charge per unit.
For instance, if the imbalance is a deficit, it would cause the currency to depreciate. The country's exports would go cheaper, resulting in an increase in demand and somewhen attaining equilibrium in the BOP.
2. Foreign exchange is unrestricted
Floating substitution rate currencies tin be traded without any restrictions, unlike currencies with fixed substitution rates. Hence, governments and banks do not demand to resort to a continuous management process.
three. Market efficiency enhances
A country'due south macroeconomic fundamentals impact the floating exchange rate in global markets, influencing the flow of portfolios between countries. Thus, floating exchange rates enhance the efficiency of the market.
4. Large foreign exchange reserves not required
For a floating exchange rate, central banks are not required to proceed large foreign currency reserve amounts for defending the exchange charge per unit. Hence, the reserves can be utilized for promoting economic growth by importing capital goods.
five. Import inflation protected
Countries with fixed commutation rates face the problem of importing inflation through surpluses of the residue of payments or higher prices of imports. Withal, countries with floating exchange rates exercise not face up such a problem.
Limitations of a Floating Substitution Rate
ane. Exposed to the volatility of the commutation charge per unit
Floating exchange rates are decumbent to fluctuations and are highly volatile past nature. A currency value against another currency may deteriorate just in one trading twenty-four hours. Furthermore, the short-term volatility in a floating exchange rate cannot be explained through macroeconomic fundamentals.
two. Restricted economic growth or recovery
The lack of control over floating exchange rates tin limit economic growth or recovery. The negative currency exchange charge per unit movements may pb to serious issues. For instance, if the dollar rises against the euro, information technology will exist more than difficult to export to the eurozone from the U.S.
3. Existing bug may worsen
If a country is suffering from economic issues, such equally unemployment or loftier inflation, floating exchange rates may intensify the existing problems. For example, depreciation of a state's currency already suffering from high inflation volition cause inflation to increment further due to an increase in demand for goods. Moreover, expensive imports may worsen the country's current business relationship.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI'southward guide on Floating Exchange Rate. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of fiscal analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below:
- Calculating the Foreign Exchange Spread
- Fixed vs. Pegged Exchange Rates
- Floating Accuse
- Hard Currency
Advantages Of Flexible Exchange Rate,
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/floating-exchange-rate/
Posted by: oconnellsilth1993.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Advantages Of Flexible Exchange Rate"
Post a Comment